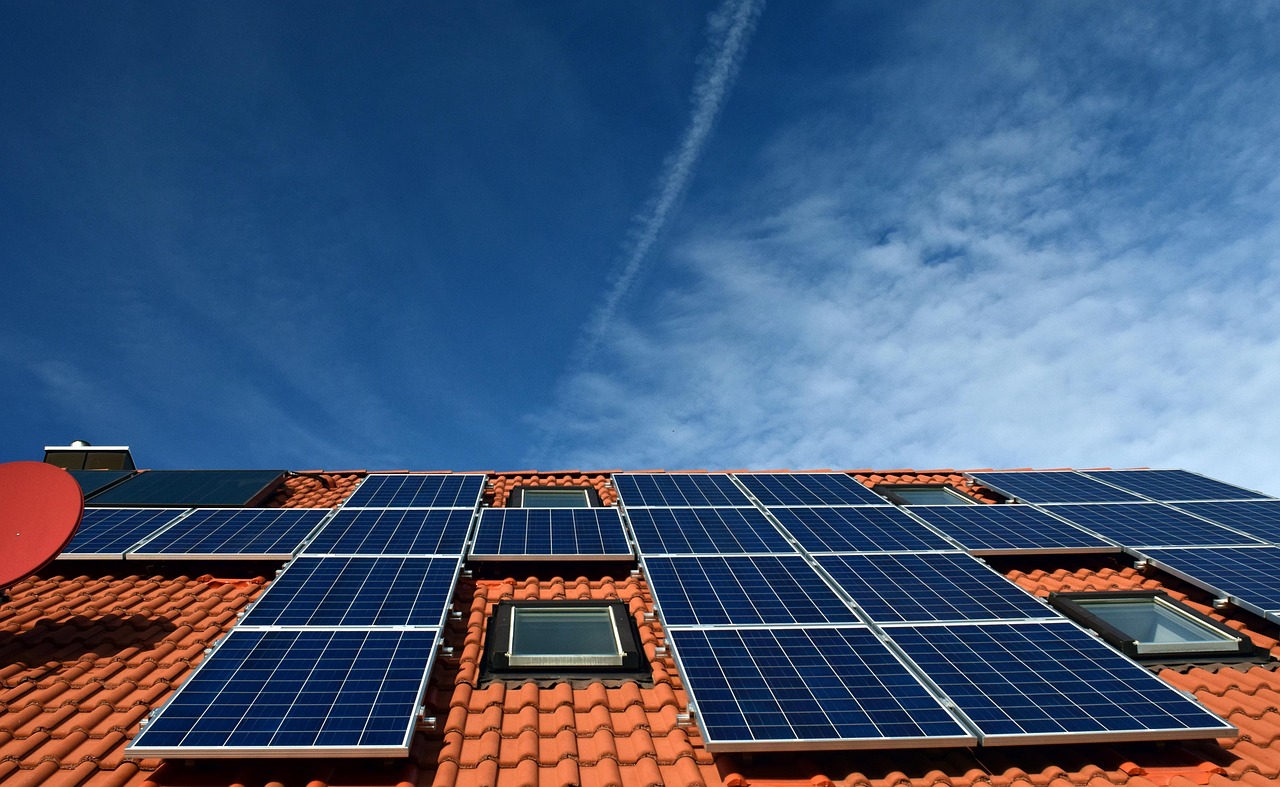
Solar glass panels transform ordinary windows into energy-generating surfaces, allowing buildings to produce electricity while maintaining natural light and aesthetics. They offer a practical solution for integrating renewable energy directly into building designs without taking up additional space. This technology is adaptable for various building types, from homes to skyscrapers, enabling a flexible approach to sustainable architecture.
By combining transparent solar cells within glass, these panels harness sunlight while remaining visually unobtrusive, making them suitable for windows, facades, and skylights. Innovations continue to improve their efficiency and storage capabilities, allowing buildings to generate and retain power even when sunlight is not available.
Understanding Solar Glass Panels
Solar glass panels are designed to protect solar cells while allowing sunlight to reach them efficiently. Different types of glass and technological features affect their durability, performance, and transparency.
This section covers how solar glass panels convert sunlight to electricity, the main types of panels available, and the key technologies that improve their function and lifespan.
How Solar Glass Panels Work
Solar glass panels use tempered glass to cover and protect the photovoltaic (PV) cells beneath. The glass must allow maximum sunlight through while shielding the cells from moisture, dust, and mechanical damage.
When sunlight hits the PV cells, photons excite electrons, creating an electric current through the photovoltaic effect. The glass does not conduct electricity but serves as a protective barrier, preventing oxidation and corrosion.
Many solar glass panels are designed with anti-reflective coatings to reduce sunlight loss. Their strength is crucial because outdoor panels face harsh weather and physical impact.
Types of Solar Glass Panels
There are two primary types of solar glass panels: glass-glass (double glass) and glass-foil.
- Glass-Glass Panels: Use tempered glass on both the front and back, offering enhanced protection from moisture and stress. Many are bifacial, capturing sunlight from both sides.
- Glass-Foil Panels: Feature glass on the front and a polymer back sheet, which is lighter but less durable and more prone to damage over time.
The choice depends on installation conditions and desired longevity. Glass-glass panels typically have a longer lifespan and better environmental resistance.
Key Technologies in Solar Glass Panels
Several technologies improve panel durability and efficiency:
- Tempered Safety Glass: About four times stronger than regular glass, it prevents breakage.
- Anti-Reflective Coatings: Increase light transmission into the cells by reducing reflection.
- UV and IR Absorbing Layers: Organic salts or films can filter ultraviolet and infrared light, protecting cells while letting visible light through.
- Bifacial Design: Allows the panel to absorb sunlight from both sides, increasing energy yield.
These technologies combined ensure solar glass panels can last in outdoor environments while maximizing energy conversion.
Applications and Benefits of Solar Glass Panels
Solar glass panels combine energy generation with structural functionality, offering multiple advantages for buildings. They improve energy efficiency, enhance design options, and fit diverse applications in both residential and commercial settings.
Residential and Commercial Uses
Solar glass panels are integrated into windows, facades, and skylights in homes and office buildings. In residential settings, they generate electricity while reducing reliance on the power grid, lowering energy bills, and increasing property value.
Commercial buildings benefit from solar glass panels through reduced operational costs and compliance with green building standards. The panels can be installed on building exteriors without compromising daylight, helping businesses meet sustainability goals without affecting workspace illumination.
These panels also protect underlying materials and extend the lifespan of the structures they cover, making them a cost-effective solution over decades.
Energy Efficiency and Performance
Solar glass panels improve energy efficiency by capturing sunlight while providing insulation. Their ability to convert solar energy directly into electricity reduces the demand for traditional energy sources.
The use of glass on both sides in some solar panels enhances light capture and durability, which results in better long-term performance. Integrated energy storage systems are increasingly common, allowing excess energy generated during daylight to be stored for later use, improving reliability.
Additionally, solar glass reduces heat transfer, lowering cooling and heating costs inside buildings while maintaining energy output.
Design and Aesthetic Advantages
Solar glass panels allow for transparent or semi-transparent installations, preserving natural light and views. This makes them suitable for windows, skylights, and curtain walls without sacrificing aesthetics.
Architects use solar glass to create sleek, modern facades that serve dual functions—energy generation and architectural expression. The material supports creative designs that blend renewable energy technologies invisibly within buildings.
The solar glass also provides UV protection and superior insulation, enhancing occupant comfort along with energy generation. This combination of functionality and appearance helps advance sustainable design in urban environments.








Leave a Reply