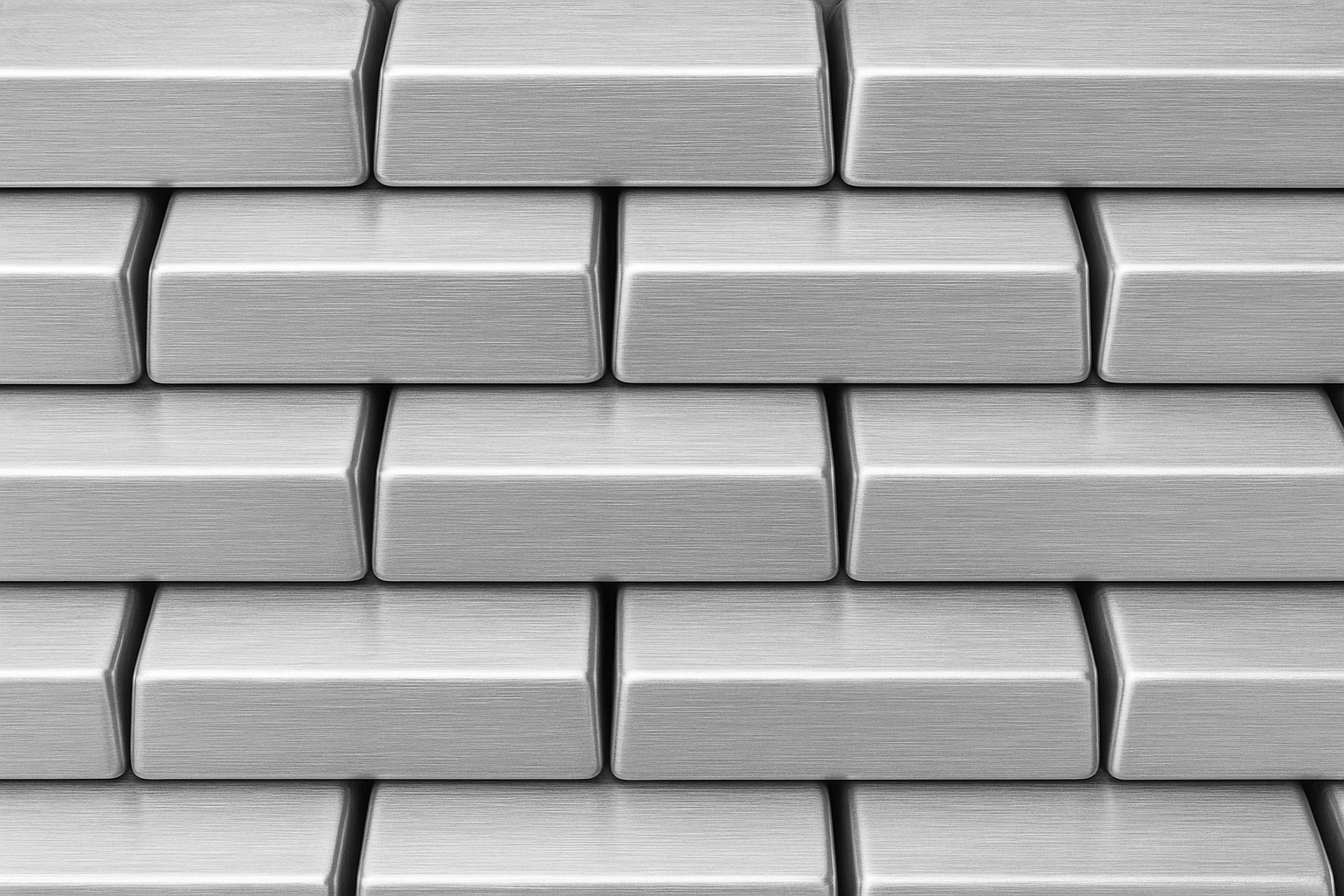
Aluminum composite panel (ACP) are widely used in modern construction and design for their lightweight, durable, and versatile properties. They consist of two thin aluminum sheets bonded to a core material, offering strength without excess weight. This combination makes ACP ideal for exterior cladding, interior decoration, and signage, providing both aesthetic appeal and functional performance.
The panels come in various sizes, finishes, and colors, allowing customization to suit different architectural needs. Their ease of installation and ability to be fabricated into diverse shapes make them a practical solution for many building projects. Manufacturers offer options such as fire-retardant cores and specialized coatings to meet specific safety and design requirements.
By blending durability with design flexibility, aluminum composite panels continue to grow in popularity across commercial and residential sectors. They provide a reliable choice for projects that demand both form and function in construction materials.
Understanding Aluminum Composite Panel
Aluminum composite panels consist of multiple layers that provide strength, durability, and flexibility. Their composition and structural design directly influence their performance in construction and design applications. Different types offer varied core materials and thicknesses to meet specific needs.
Composition and Structure
Aluminum composite panels are made by sandwiching a non-aluminum core between two thin aluminum sheets. The aluminum layers provide rigidity, corrosion resistance, and a smooth finish.
The core material varies, commonly including polyethylene or a fire-resistant mineral core. This core gives the panel its lightweight quality and thermal insulation properties while maintaining structural integrity.
Panels typically range from 3mm to 6mm in thickness, which affects flexibility and strength. The bonding process ensures the aluminum sheets and core work together to deliver stability and impact resistance.
Key Properties and Benefits
Aluminum composite panels are lightweight yet strong, reducing the load on supporting structures. Their smooth surface allows for easy cleaning and customization with various finishes, including coatings resistant to weather and UV damage.
They offer excellent durability against corrosion and environmental wear, making them suitable for outdoor cladding and signage. Thermal insulation and fire-retardant options enhance safety and energy efficiency.
The material’s flexibility enables curved and flat installations. Additionally, aluminum composite panels provide noise reduction and ease of maintenance, benefiting both architects and building owners.
Types of Aluminum Composite Panel
There are primarily two types based on the core: polyethylene (PE) core and fire-resistant (FR) mineral core. PE core panels are lightweight and cost-effective but less fire-resistant.
FR panels have mineral cores that enhance fire safety, complying with stricter building regulations, especially in high-rise constructions. These panels tend to be heavier and more expensive.
Thickness and surface finishes also differentiate types. Options include PVDF coating for color retention and anodized finishes for increased resistance. Depending on the application, various grades and standards guide the choice of panel type.
Applications and Installation
Aluminum composite panels (ACPs) are valued for their versatility in various building projects. They serve multiple functions from decorative facades to protective cladding. Proper installation techniques ensure durability and maintain the panels’ aesthetic appeal. Regular maintenance extends their service life significantly.
Architectural Uses
ACPs are widely used in exterior cladding for commercial and residential buildings. Their lightweight nature makes them suitable for curtain walls, soffits, and entrances. The panels offer design flexibility with options for different colors, finishes, and textures.
They also appear in signage, interior wall coverings, and partitions due to their smooth surface and easy customization. ACPs serve functional and aesthetic purposes, contributing to energy efficiency and weather resistance. Fire-retardant core options further enhance safety in public spaces.
Installation Techniques
Installation starts with precise measurement and planning to avoid errors. The panels are cut using specialized tools, ensuring clean edges. Mounting involves fixing the panels onto a framework with fasteners or adhesive systems designed for metal materials.
A weatherproofing step is critical. Sealants and proper overlaps prevent water infiltration and air leaks. Installers must allow for thermal expansion to avoid warping or cracking over time. Following manufacturer guidelines on material handling and fastening is essential for a lasting facade.
Maintenance and Longevity
Maintenance revolves around regular cleaning and inspection. ACPs require non-abrasive cleaning agents to avoid surface damage. Periodic checks for loose fasteners or dents help catch issues early.
Repairs often involve panel replacement or resealing joints. The panels resist fading and corrosion but may degrade if exposed to harsh chemicals or extreme conditions. Proper maintenance can extend ACP lifespan to 20 years or more, preserving both function and appearance.








Leave a Reply